Homeprepositions
prepositions
Adjectives
Mixed Adjectives
Test Your Adjective Knowledge with Our Fun and Engaging Adjectives Quiz.
What are Prepositions? Function and Usage | Different Types of Preposition | Examples & Notes
Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. They usually indicate where something is in relation to something else.
Here are some examples to help you remember:
“The cat is on the table,” the preposition “on” shows the relationship between the cat and the table.
Prepositions are essential in constructing sentences in English. They make the sentences clearer and more precise by indicating thetime, place, and direction of an action. They also help convey more information about a sentence’s subject and object, and establish the connection between them.
Prepositions can be classified as simple or complex. Simple prepositions include words like “in”, “on”, “at”, “with”, “for”, and “to” Complex prepositions are made up of more than one word, such as “in front of” “on top of”, and “next to”.
Using prepositions correctly is crucial in conveying the intended meaning of a sentence. A common mistake people make is using the wrong preposition or leaving them out altogether.
For example,
“I will meet you the park,” should be “I will meet you at the park.”
Time prepositions
Time prepositions are a type of preposition(e.g. after, before, during) that are used to describe a specific time or duration. They are commonly used to indicate when something happened or will happen.
For example,
“I woke up at 7 o’clock this morning.”
“We’ll be finished by noon.”
Some common time prepositions include:
at (used for specific times, such as “at 9 AM”)
on (used for specific dates, such as “on July 4th” or for days of the week, such as “on Monday”)
in (used for longer periods of time, such as “in the morning” or “in March”)
Time prepositions can be used in a variety of ways to give context to a sentence.
Here are a few more examples:
“I’ll be ready to leave in a few minutes.”
“The train will arrive at the station in five hours.”
“We always have lunch at noon.”
Place prepositions
Place prepositions are a type of preposition that are used to describe the location or position of something or someone. They are commonly used to give information about where an action is taking place or where an object is located.
For example,
“The book is on the table.”
“I’m going the store.”
“The cat is under the bed.”
Some commonplace prepositions include:
in (used for enclosed spaces, such as “in the room” or “in the car”)
on (used for surfaces, such as “on the table” or “on the wall”)
at (used for specific points, such as “at the corner” or “at the park”)
Place prepositions can be used in a variety of ways to give context to a sentence
Here are a few more examples:
“The restaurant is across the street.”
“The airplane is above the clouds.”
“The ball rolled beneath the couch.”
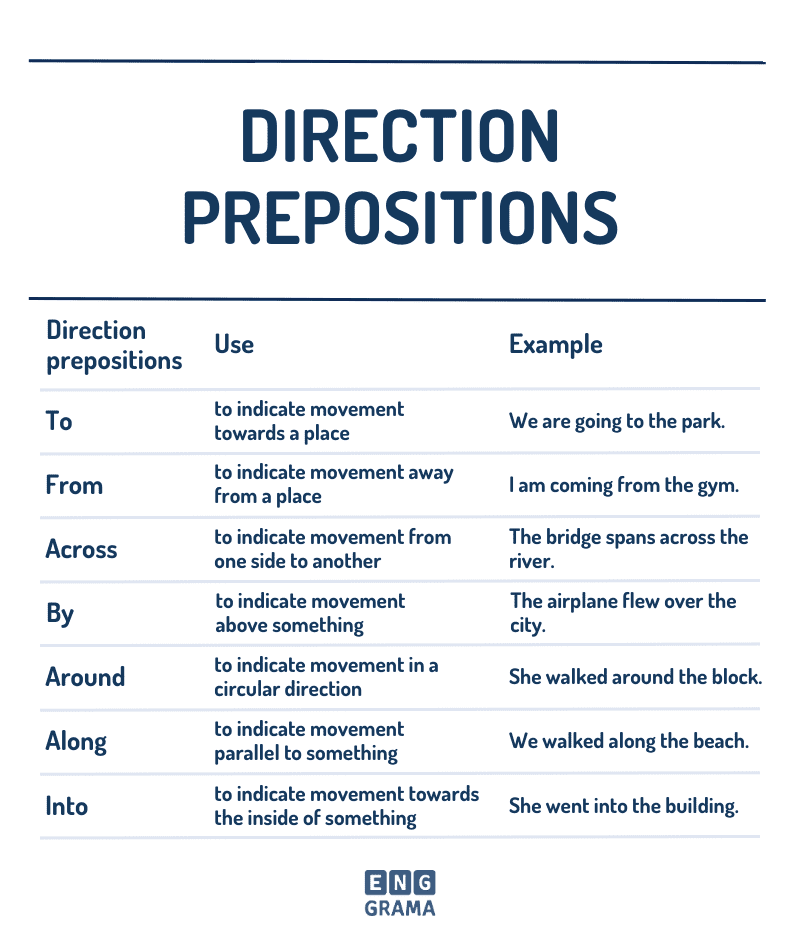
Direction prepositions
Direction prepositions are a type of preposition that are used to describe movement or direction. They are used to give information about where something or someone is going or coming from.
For example,
“I’m walking toward the door.”
“The train is heading south.”
“The bird flew over the tree.”
Some common direction prepositions include:
to (used for a destination, such as “to the store” or “to the park”)
from (used for a starting point, such as “from the airport” or “from the office”)
into (used to describe movement from outside to inside, such as “into the house”)
Direction prepositions can be used in a variety of ways to give context to a sentence.
Here are a few more examples:
“The car turned left onto the street.”
“She jumped off the diving board into the pool.”
“The bus is coming toward us from the other side of the street.”
In summary,
Direction prepositions are a type of preposition that is used to describe movement or direction.
Agent prepositions
Prepositions of the type “agent” denote the person who is carrying out the activity. They are often used in connection with a passive verb to specify the reason for the activity.
Below we have provided some examples:
“The vase was broken by the cat.”
“The building was built by the construction company.”
“The book was written by a famous author.”
As you can see from these examples, the agent preposition is used to indicate who or what is responsible for the action in the sentence.
Some common agent prepositions include:
by (used to indicate the doer of an action, as in the examples above)
with (used to indicate the means by which an action is done, as in “He painted the wall with a brush.”)
Agent prepositions can be used in various ways to give context to a sentence
Here are a few more examples:
“The meal was cooked by the chef.”
“The car was repaired by the mechanic.”
“The cake was decorated with frosting by the baker.”
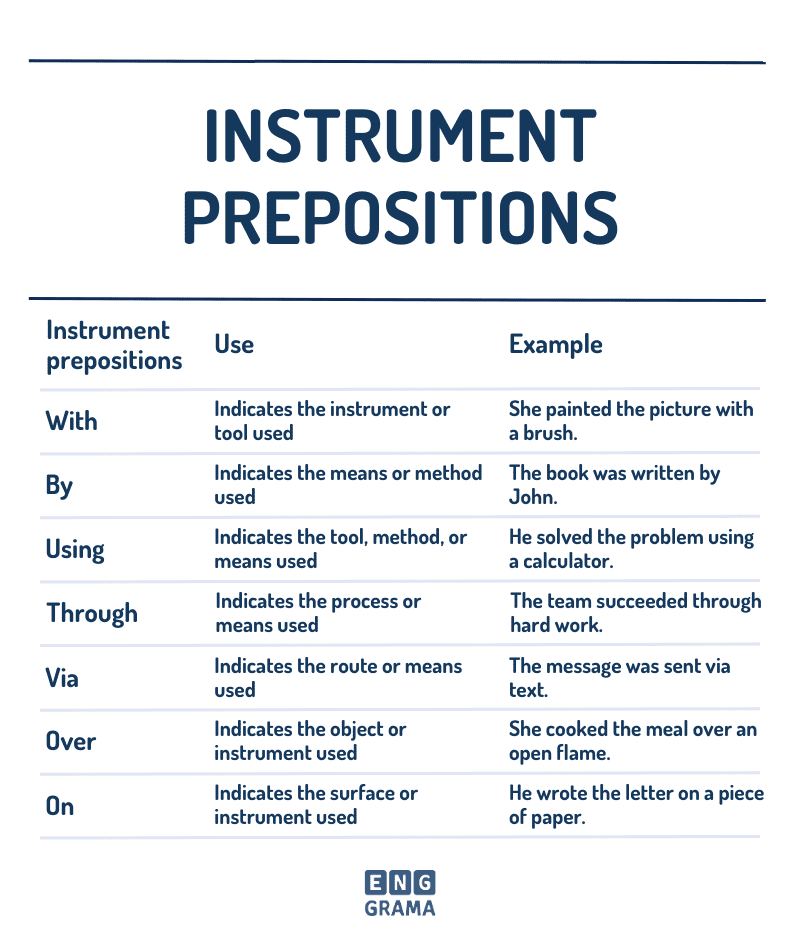
Instrument prepositions
Instrument prepositions are a type of preposition that indicate the tool or means by which an action is performed. They often appear in a sentence with a passive verb to show the tool that was used in performing the action.
Below we have provided some examples:
“The cake was cut with a knife.”
“The picture was painted with a brush.”
“The wall was drilled with a drill.”
As you can see from these examples, the instrument preposition is used to show what tool or means was used in performing the action in the sentence.
Some common instrument prepositions include:
with (used to indicate the tool or means by which an action is done, as in the examples above)
by (used to indicate the doer of an action, as in the examples for agent prepositions)
“The salad was chopped with a knife.”
“The letter was written with a pen.”
“The hair was styled with a brush.”
In summary,
Instrument prepositions are a type of preposition that indicate the tool or means by which an action is performed.
Manner Prepositions
Prepositions are words that connect nouns and pronouns to other words in a sentence, indicating the relationship between them ( by, with, by, through, in, on, at, over, and so on). Manner prepositions are a specific type of preposition that indicate how something is done.
Let’s take a closer look at the manner of prepositions in the below examples:
for the preposition “With”
The preposition “with” is often used to show how someone is using a tool or object.
For example
She was cutting the cake with a chainsaw.
He was driving the car with his feet.
for the preposition “By”
The preposition “by” is used to indicate the method or means by which something is done
For example
She learned to swim by watching videos on YouTube.
He won the race by cheating.
or the preposition “Through”
The preposition “through” indicates that something is done using a process or system.
For example
She got a job at the company through her connections.
He solved the puzzle through trial and error.
for the preposition “In”
The preposition “in” is often used to show how something is done in a certain manner or style.
For example
She dances in a very graceful manner.
He writes in a very humorous style.
for the preposition “On”
The preposition “on” is often used to indicate the method or way in which something is done, especially when it involves communication or interaction with others.
For example
She apologized on bended knee.
He proposed to her on a hot air balloon.
Purpose prepositions
Prepositions are important words that help to connect nouns and pronouns to other words in a sentence. Purpose prepositions are a specific type of preposition that indicate the intended use or purpose of something.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at purpose prepositions and how you can use them correctly and creatively in your writing.
For
The preposition “for” is often used to indicate the intended purpose of an object or action.
For example
She bought a cake for the party.
He went to the gym for exercise.
To
The preposition “to” is used to indicate the intended recipient of an action or object.
For example
She wrote a letter to her friend.
He gave the present to his mother.
For example
She studied hard in order to pass the test.
He saved money in order to buy a car.
So that
The phrase “so that” is used to indicate the purpose or intended result of an action.
For example
She practiced the piano every day so that she could become a better musician.
He woke up early so that he could finish his work on time.
With the aim of
The phrase “with the aim of” is used to indicate the intended goal or purpose of an action.
For example
She started a new business with the aim of making a profit.
He began writing a book with the aim of becoming a best-selling author.
With a view to
The phrase “with a view to” is used to indicate the intended outcome or purpose of an action.
For example
She enrolled in a cooking class with a view to improving her culinary skills.
He began exercising regularly with a view to improving his health.
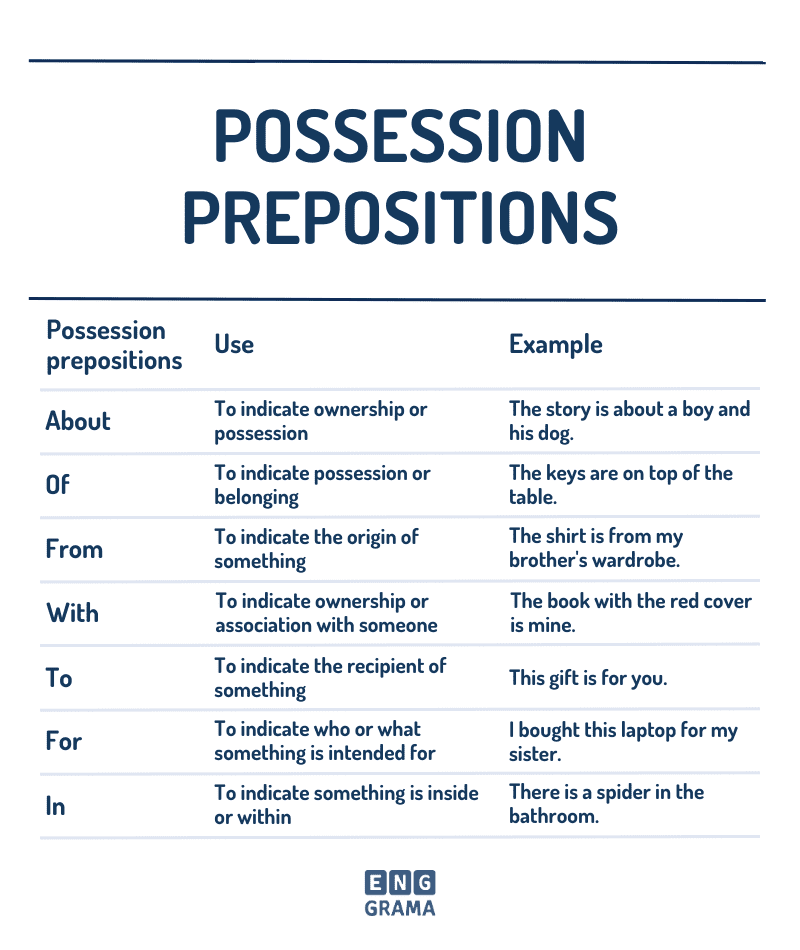
Possession prepositions
Possession prepositions are words that show who owns or has something. Some common possession prepositions are “of”, “‘s”, and “s'”.
For example, if you say “the tail of the cat”, “of” shows that the tail belongs to the cat. If you say “Ram’s car”, “‘s” shows that the car belongs to Ram.
Below we have mentioned some examples of possession prepositions that help you to understand in a better manner:
If you say “the dog’s bed is bigger than mine”, “‘s” shows that the bed belongs to the dog.
If you say “I brought pizza for everyone”, “for” shows that the pizza is meant for everyone to share.
If you say “the girl with the red hair”, “with” shows that the girl has red hair.
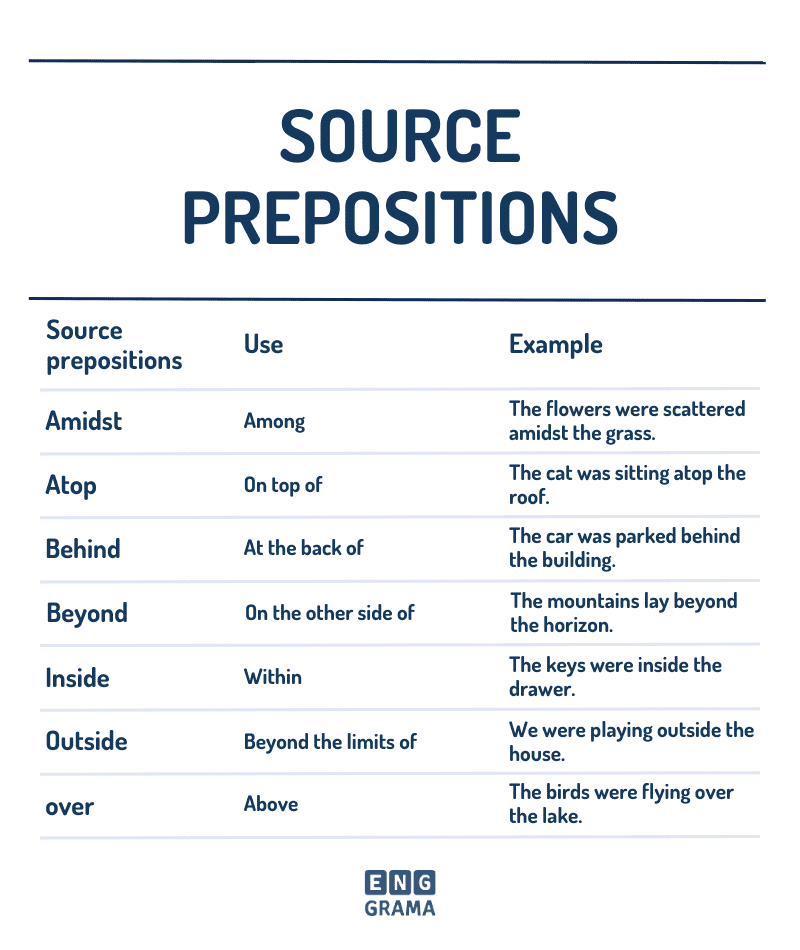
Source prepositions
Source prepositions are words that show where something comes from. Some common source prepositions are “from”, “out of”, and “off”.
For example, if you say “the gift is from my mom”, “from” shows that the gift came from the speaker’s mom. If you say “I’m out of milk”, “out of” shows that there is no more milk left.
Here are some examples to help you understand how to use source prepositions:
If you say “the cake is from outer space”, “from” shows that the cake came from a very faraway place.
If you say “I’m out of ideas for jokes”, “out of” shows that there are no more ideas left.
If you say “the cat fell off the table again”, “off” shows that the cat was on the table and then fell.
Below we have mentioned some examples of source prepositions that help you to understand in a better manner:
“I crawled out of bed this morning.” (out of bed)
“The dog ran from the house.” (from the house)
“The bird flew out of the cage.” (out of the cage)
“I emerged from my blanket cocoon.” (from my blanket cocoon)
“The clown popped out of the tiny car.” (out of the tiny car)
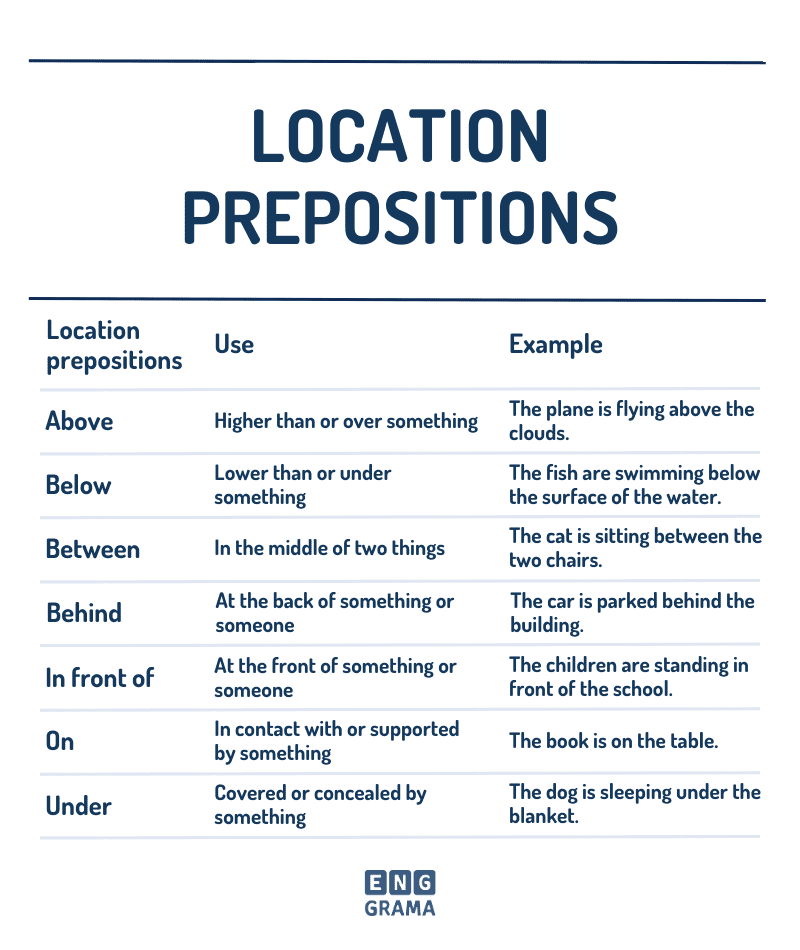
Location prepositions
A Guide to Using “In”, “On” and “At” in English. If you’re learning English, one of the trickiest parts can be understanding location prepositions. These words describe the position of people, objects, and actions in relation to other things.
Using “In” to Describe Enclosed Spaces
The preposition “in” is used to describe a location that is enclosed or surrounded by something.
For example, you might say:
“The cat is in the box” to indicate that the cat is surrounded by the box.
Similarly,
You would say “I’m in the shower” to indicate that you’re enclosed by the shower. “In” can also be used to describe areas within larger spaces, such as “in the city”, “in the park”, or “in the classroom”.
Using “On” to Describe Surfaces and Flat Objects
The preposition “on” is used to describe a location that is a surface or flat object.
For example, you might say:
“The book is on the table” to indicate that the book is resting on the surface of the table.
Similarly,
You would say “the spider is on my hand” to indicate that the spider is on the surface of your hand. “On” can also be used to describe locations that are specific points on a larger surface, such as “on the beach”, “on the road” or “on the roof”.
Using “At” to Describe Specific Locations or Points in Space
The preposition “at” is used to describe a specific location or a point in space.
For example, you might say:
“I’ll meet you at the movie theater” to indicate a specific location.
Similarly,
“The ball hit me at the top of my head” to indicate a specific point in space.
“At” can also be used to describe locations that are more general, but still distinct, such as “at home”, “at work” or “at school”.
To help you remember which preposition to use in different situations, here are some examples
“I’m in a pickle” (meaning you’re in a difficult situation)
“I’m on top of the world” (meaning you’re incredibly happy)
“I’m at the end of my rope” (meaning you’re at the limit of your patience)
“The cat is in the bag” (meaning a secret has been revealed)
“The ball is on the roof” (meaning a situation is difficult)
(FAQs) About Prepositions
To Practice and Improve Your Skills,